Have you ever heard of a Zinc Ionophore? The definition of an Ionophore is, “a substance which is able to transport particular ions, like zinc, across a lipid membrane in a cell”. Well, now is the time why knowing more about zinc and a Zinc Ionophore compound may just save a life, especially someone with COVID-19. Zinc, selenium, vitamin D, and Zinc Ionophore supplementation via dietary supplements and/or food sources (oyster, liver…), sunshine (UVB) exposure are more important than ever to have dialed-in. Cellular health, especially the lung, and proper immune function are all dependant on adequate zinc levels, in one way or another.
Low zinc status whether caused by the virus (inflammation and/or treatment), or as a preexisting condition, which is very common, may increase the susceptibility to develop symptoms if exposed to COVID-19, increase the severity of COVID-19 symptoms, as well as speed its progression leading to death.
Going on a ventilator is the fastest route to death for anyone with the virus and ANY preexisting condition, such as but not limited to diabetes, obesity, sickle cell anemia, heart disease, renal disease, kidney disease, low selenium, low vitamin D, low zinc, anemia, low hemoglobin, thalassemia, emphysema, smoking, elevated blood glucose, and elevated A1C.
Plasma zinc has been shown to be a strong predictor of hemoglobin, independent of iron status, in 2 previous studies (9, 10). Zinc may affect hemoglobin via several zinc-dependent enzyme systems involved in hemoglobin synthesis (11) and erythropoiesis stimulation (12).
Plasma selenium has also been positively associated with hemoglobin in studies among the elderly in the United Kingdom (13) and United States (14) and in children in Vietnam (15–17) and northeast Brazil (18). Possible mechanisms whereby low selenium status could potentially contribute to low hemoglobin concentrations include the role of selenium as a potent antioxidant in erythrocytes (19) and in the maintenance of optimal immune function—and thus in the anemia of chronic inflammation (20). Low plasma selenium concentrations also have the potential to compromise zinc status (21, 22) and hence may have an indirect negative impact on hemoglobin by the mechanisms outlined previously.
A link between vitamin D deficiency and low hemoglobin concentrations or anemia in children is not as well characterized (23–25). Such a relation was first observed clinically in adults with end-stage heart failure, diabetes, and chronic kidney disease (pre-existing conditions that cause COVID-19 patients a higher level of morbidity). and then subsequently in otherwise healthy adults (26, 27). The mechanism is uncertain but may be at least partly related to the interaction between calcitriol (1,25-dihydroxvitamin D3) and myeloid zinc finger-1, which is known to play a critical role in hematopoiesis and myeloid cell differentiation (28).
The functional role of intracellular labile zinc in pulmonary endothelium
After iron, zinc is the most abundant essential trace metal. Intracellular zinc ([Zn](i)) is maintained across a wide range of cells and species in a tight quota (100 to 500 μM) by a dynamic process of transport, intracellular vesicular storage, and binding to a large number of proteins (estimated at 3-10% of human proteome). As such, zinc is an integral component of numerous metalloenzymes, structural proteins, and transcription factors. It is generally assumed that a vanishingly small component of [Zn](i,) referred to as free or labile zinc, and operationally defined as the pool sensitive to chelation and capable of detection by a variety of chemical and genetic sensors, participates in signal transduction pathways. Zinc deficiencies, per se, can arise from acquired (malnutrition, alcoholism) or genetic (mutations in molecules affecting zinc homeostasis, the informative and first example being acrodermatitis enteropathica) factors or as a component of various diseases (e.g., sickle cell disease, cystic fibrosis, sepsis). Hypozincemia has profound effects on developing humans, and all facets of physiological function (neuronal, endocrine, immunological) are affected, although considerably less is known regarding cardiovascular pathophysiology. In this review, we provide an update on current knowledge of molecular and cellular aspects of zinc homeostasis and then focus on implications of zinc signaling in pulmonary endothelium as it relates to programmed cell death, altered contractility, and septic and aseptic injury to this segment of the lung.
Several studies have demonstrated that zinc deficiency sensitizes the lung to acute injury. In particular, dietary restriction led to enhanced sensitivity to polymicrobial sepsis and hyperoxic lung injury (COVID-19 patients of ventilators = Hyperoxic Lung Injury) “Exposure to high levels of oxygen (hyperoxia) is common in critically ill patients and can be associated with the development of acute lung injury (ALI). Prolonged exposure to hyperoxia results in the local generation of reactive oxygen species, which can lead to damage to viable tissue.”
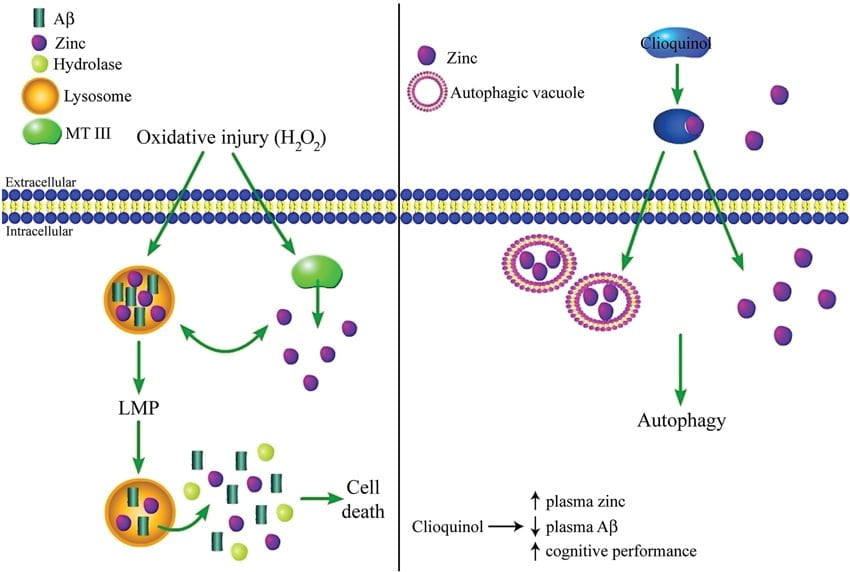
Labile (free) zinc, a tiny fraction of total intracellular zinc that is loosely bound to proteins and easily interchangeable, modulates the activity of numerous signaling and metabolic pathways. Dietary plant polyphenols such as the flavonoids quercetin (QCT) and epigallocatechin-gallate (EGCG – green tea extract) act as antioxidants and as signaling molecules. Remarkably, the activities of numerous enzymes that are targeted by polyphenols are dependent on zinc. We have previously shown that these polyphenols chelate zinc cations and hypothesized that these flavonoids might be also acting as zinc ionophores, transporting zinc cations through the plasma membrane. To prove this hypothesis, herein, we have demonstrated the capacity of quercetin (QCT) and epigallocatechin-gallate to rapidly increase labile zinc in mouse hepatocarcinoma Hepa 1-6 cells as well as, for the first time, in liposomes. In order to confirm that the polyphenols transport zinc cations across the plasma membrane independently of plasma membrane zinc transporters, quercetin (QCT), epigallocatechin-gallate, or clioquinol (CQ), alone and combined with zinc. Only the combinations of the chelators with zinc triggered a rapid increase of FluoZin-3 fluorescence within the liposomes, thus demonstrating the ionophore action of quercetin (QCT,) epigallocatechin-gallate, and CQ on lipid membrane systems. The ionophore activity of dietary polyphenols may underlay the raising of labile zinc levels triggered in cells by polyphenols and thus many of their biological actions.
There you have it. Zinc and supplementing with a Zinc Ionophore (quercetin zinc ionophore) can be an important adjunct for one’s health. Better life through nature’s chemistry.
Additional Reading:
Would ivermectin serve as a conductor for the zinc as well? Any better than Quercetin?
Pam,
Ivermectin is a zinc ionophore. I’m not aware of any research comparing the two.
Respectfully,
Dr. Ettinger
Dr V. Zelinco via his Zelinco Protocal. States Quercitin is like a 20 cal hand pistol and Ivermectin and Hydrocloriquin are like 50 caliber machine guns.
Does the type of Quercitin matter? The bioavailability of the various forms vary considerably, which might affect dosage requirements?
Philip,
Quercetin is very safe. I have been taking a heaping 1/2 – 1 tsp for over a year now. I get mine from bulksupplements.com as the powder is always cheaper than caps. I just dose it by how I’m feeling and how many sick people I treat each week. I also take pine back extract, resveratrol, curcumin 95, and grape seed extract from bulksupplements.com
I hope this helps.
Dr. Ettinger
What are the dosage amounts you recommend for zinc, and what type? Dosage amounts for quercitin? What would be a good protocol for all your recommendations? Thank you
I’m sorry but I can’t give dosage or protocol recommendations to non-patients due to liability reasons.
What is a zinc ionophore which will not cause the blood to thin? My husband has been prescribed Eliquis for the next 5 months due to “numerous small blood clots” in his lungs. He took two Moderna injections in February.
Zinc Ionophore Activity of Quercetin and Epigallocatechin-gallate: From Hepa 1-6 Cells to a Liposome Model
Labile (free) zinc, a tiny fraction of total intracellular zinc that is loosely bound to proteins and easily interchangeable, modulates the activity of numerous signaling and metabolic pathways. Dietary plant polyphenols such as the flavonoids quercetin (QCT) and epigallocatechin-gallate (EGCG – green tea extract) act as antioxidants and as signaling molecules. Remarkably, the activities of numerous enzymes that are targeted by polyphenols are dependent on zinc. We have previously shown that these polyphenols chelate zinc cations and hypothesized that these flavonoids might be also acting as zinc ionophores, transporting zinc cations through the plasma membrane. To prove this hypothesis, herein, we have demonstrated the capacity of quercetin (QCT) and epigallocatechin-gallate to rapidly increase labile zinc in mouse hepatocarcinoma Hepa 1-6 cells as well as, for the first time, in liposomes. In order to confirm that the polyphenols transport zinc cations across the plasma membrane independently of plasma membrane zinc transporters, quercetin (QCT), epigallocatechin-gallate, or clioquinol (CQ), alone and combined with zinc. Only the combinations of the chelators with zinc triggered a rapid increase of FluoZin-3 fluorescence within the liposomes, thus demonstrating the ionophore action of quercetin (QCT,) epigallocatechin-gallate, and CQ on lipid membrane systems. The ionophore activity of dietary polyphenols may underlay the raising of labile zinc levels triggered in cells by polyphenols and thus many of their biological actions.
Dr. Ettinger,
If a person takes zinc ionophores, would you need to take a quercetin vitamin also?
Sharon,
It wouldn’t hurt.
Respectfully,
Dr. Ettinger
1 – If I get stomach upset with ingestion of pineapple, is this caused by bromelain in the pineapple? I question this because it is compounded with all the quercetin products I’ve seen. (My daughter has the same problem)
I suppose I. Ould break open a capsule and try small amounts initially, to test my reaction.
Richard,
N=1 experimentation would help to uncover the why. Also, quercetin can be found with no additives. I use http://www.bulksupplements.com
Respectfully,
Dr. Ettinger
Dr. Ettinger;
Wow..
I was searching for a Zinc Ionophore and came up here with your comprehensive recommendations.
I tried to clear a prescription of hydroxychloroquine in advance with my Doctor, but he seems caught up in the politics rather than the track record of the medication.
Additionally, as my Wife is Diabetic, the HCQ is not an option for her, and your regimen seems to fill all the requirements without additional risks.
Thank you for taking the time to share this information, and I will keep your contact information handy should I find myself in the Covid battle.
Mark
Your welcome.
Thank you so much, Dr. E! I have been wondering about natural Zn ionophores. I truly appreciate your research.
Ari,
Thank you and you are welcome.
Dr. Ettinger
Wow great article.
Lee,
Thank you very much!
Dr. Ettinger
I have chest pain and stomach pain…. h-pylori positive by endoscopy then negative second time round in February. I keep spiking a temp am malnourished even though I eat a great diet… stomach pain prevents me from eating all I want to eat. My question is should I pursue quad therapy at this time with the virus going around … or should I go and get tested and risk getting exposed? I have Candida as well but nystatin seems to mess with me more.
Zara,
I can’t make a recommendation for you. That is between you and your doctor.
I’m not sure if you have seen any of my H. pylori posts. I have been treating H. pylori patients around the world since 2008. https://advancedhealing.com/biofilm-protocol-for-lyme-and-gut-pathogens/
If the follow-up biopsy was negative, why would you treat it again? If you think it may still be there do a follow-up breath test to confirm. H. pylori is rarely the generator of every stomach/GI symptom one experiences. This means that just because it’s gone does not mean your symptoms will necessarily be gone.
As far as Pylera goes – doing a crazy strong ABx protocol now would not be recommended for anyone unless their life depended upon it.
Lastly I have been helping patients for 31 years now, treating them in my office and around the world via video consultations. If you are looking for help with your stomach/GI issues, I can do that. I would create a tailored protocol that fits your needs, based on human physiology, your labs, history, lifestyle… Here is a link to my website. “New Patients/Forms” section has my policies and fees. https://advancedhealing.com/
Respectfully,
Dr. Ettinger