In my professional opinion, based on over three decades of research and clinical practice, those who have the highest vitamin D levels from the sun, not supplementation, have the lowest all-cause mortality risk.
In simple terms, it means that those who get the most sun exposure on their skin have the least chance of developing and dying from every form of disease.
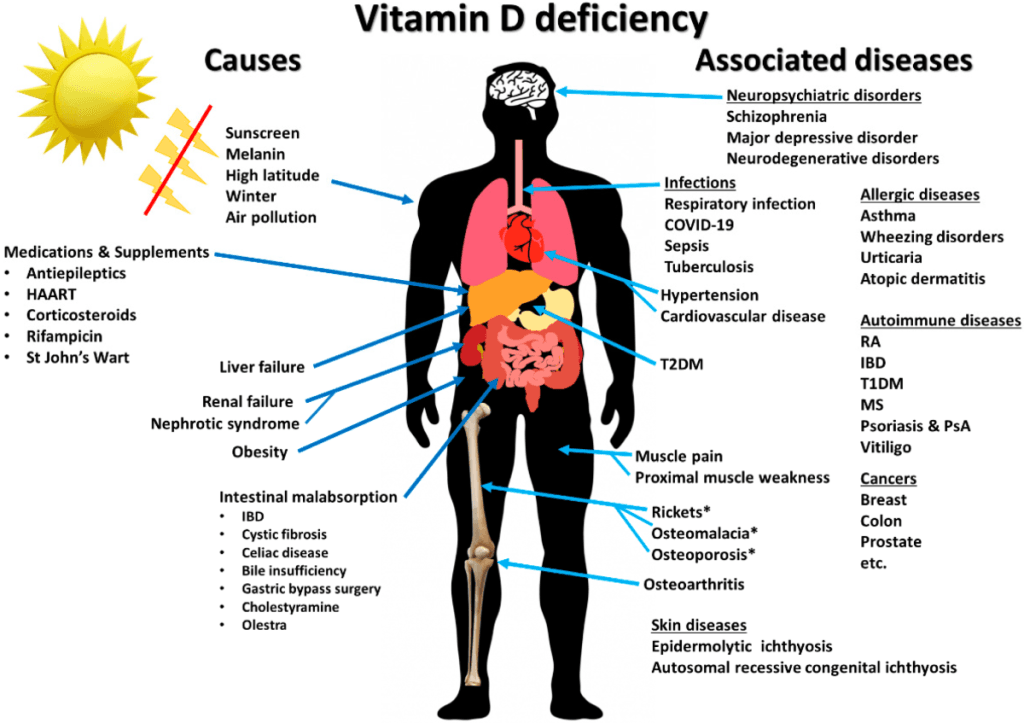
Vitamin D deficiency, overall and cause-specific mortality: the impact of age – https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0398762018307922
Any study that simply measures vitamin D levels and then concludes that vitamin D is the reason for reduced mortality is flawed. 90% of vitamin D in the blood is produced by the skin after exposure to the sun. But sun exposure also leads to the production of many photo-products beyond vitamin D, such as nitric oxide, serotonin, endorphin, brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), and dopamine. Non-supplemented vitamin D levels are nothing more than a surrogate measurement for sun exposure. Here are some facts about sun exposure that may or may not be due to vitamin D:
-
- Seventy-five percent of melanomas occur in areas of the body that are seldom or never exposed to the sun. #Melanoma #Cancer
- Women who sunbathe regularly have half the risk of death during a 20-year period compared to those who stay indoors.
- Multiple sclerosis (MS) is highest in areas of little sunlight and virtually disappears in areas of year-round direct sunlight.
- A Spanish study shows that women who seek the sun have one-eleventh of the hip fracture risk as sun avoiders.
- Men who work outdoors have half the risk of melanoma as those who work indoors. #Melanoma #Cancer
- Women who avoid the sun have ten times the risk of breast cancer than those who embrace the sun. #Cancer
- Sun exposure decreases heart disease risk.
- Sun exposure dramatically improves mood.
- Those persons who spend many hours daily outdoors have only 1/50 the risk of Parkinson’s disease!
- For each death caused by diseases associated with sun exposure, there are 328 deaths caused by diseases associated with sun deprivation.
- Sun exposure increases the production of BDNF, which is essential to nerve function.
- Sun exposure can produce as much as 20,000 IU of vitamin D in 20 minutes of full-body sun exposure.
- In the U.S., vitamin D deficiency in children has increased by 83 times during a 14-year period. That is likely due to indoor living and sunscreen use.
Are you frustrated by your doctor not actually knowing why you don’t feel well?
I understand health and disease. It’s been my job, hobby, and passion for 34+ years.
For the first time, let’s fix the problem and stop treating or masking symptoms.
No Obligation, 15-minute, Phone Consultation*
*Please call me today to schedule your complimentary 15-minute phone consultation. Let’s see if you and I are a good fit. I truly want you to feel both excited and confident that I have an understanding of your situation and a plan that’s right for you. I look forward to hearing from you at 714-639-4360.

What is the best way to obtain enough sunlight in cold climates where we are bundled up for half the year? What is the minimum beneficial amount of sunlight daily? I read that our eyes can take in and produce more vitamin D even than our skin and that this is one reason why sunglasses are bad for us. Is this true? If so, is eye exposure to sunlight in winter enough to get and keep levels up? If not, please advise on a better method/option? Thank you so much!
Becky,
I appreciate your questions and curiosity. I wish I had time to write an essay for you. All of that data is here and why I created this space – https://www.patreon.com/DrMarcusEttinger
Respectfully,
Dr. Ettinger
All above sounds correct.
Above does not mean that all who do not want to die should relocate to Equator.
We need a means to figure out when we should get off the sun and look for a shade or find out a way to find out one’s preferable latitude.
Vitamin D is made from HDL cholesterol.
Need to figure out if we have sufficient HDL, and details on how to adjust it to the desirable levels.
(Omega-6)/(Omega-3) currently and for about last 150 years, is MASSIVELY being screwed worldwide.
Seed oils contain massive amounts of Linoleic acid. 20, 40 or 560 times more than we ate between KT event multimillion years ago until about 150 years ago.
That seed oil is being eaten not only by us but also by animals, seafood and birds that we raise for our food.
That seed oil is the reason for all neolitic diseases that nobody new about 150 years ago and the growth from one generation to the next.
Amen, brother.
How to improve HDL levels: More MUFA’s, Exercise, Sunshine, and Lecithin.
– Exercise stimulates the activity of several enzymes that can enhance HDL metabolism and contribute to higher concentrations of HDL cholesterol. Two key enzymes involved in HDL metabolism are:
– Lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT): LCAT is an enzyme responsible for the esterification of cholesterol in the HDL particle. During exercise, the activity of LCAT can increase, promoting the conversion of free cholesterol to cholesterol esters. This process helps in the maturation and remodeling of HDL particles, facilitating their role in reverse cholesterol transport. LCAT contain phospholipids, primarily adequate phosphatidylcholine (organic, free-range eggs; and organic, grass-fed beef).
– Lipoprotein lipase (LPL): LPL is an enzyme found in tissues such as skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. It plays a crucial role in the breakdown of triglycerides in circulating lipoproteins, including HDL. During exercise, the activity of LPL increases, leading to the hydrolysis of triglycerides in HDL, which results in the generation of free fatty acids and promotes HDL maturation and remodeling.
– By stimulating the activity of LCAT and LPL, exercise helps to improve the functionality and composition of HDL particles, leading to higher concentrations of HDL cholesterol. Additionally, exercise has other favorable effects on lipid metabolism, such as increasing the expression of ATP-binding cassette transporters, which are involved in cholesterol efflux from peripheral tissues to HDL.