Part 1 – What are GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1) and PYY (Peptide YY), Their Differences and Similarities, and How to Stimulate Them with Diet and Lifestyle Modifications for Improved Health and Weight Control?
Part -2 (Coming Soon) – Ozempic, Trulicity, Wegovy, and Victoza vs Nature for Weight Management and Overall Health
Part 3 (Coming Soon) – The SIBO (IBS), Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S gas), and GLP-1 Connection
Introduction
In the quest for better health and effective weight management, understanding the roles of specific hormones in our bodies can be incredibly beneficial. Two such hormones, GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1) and PYY (Peptide YY), have garnered significant attention due to their profound impacts on appetite regulation and metabolism. This blog post delves into what GLP-1 and PYY are, their differences and similarities, and practical ways to upregulate them through diet and lifestyle modifications for improved health and weight control.
Table of Contents
- Understanding GLP-1
- Understanding PYY
- Differences Between GLP-1 and PYY
- Similarities Between GLP-1 and PYY
- Dietary Ways to Upregulate GLP-1 and PYY
- Lifestyle Modifications to Enhance GLP-1 and PYY Levels
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
- References
Understanding GLP-1
What is GLP-1?
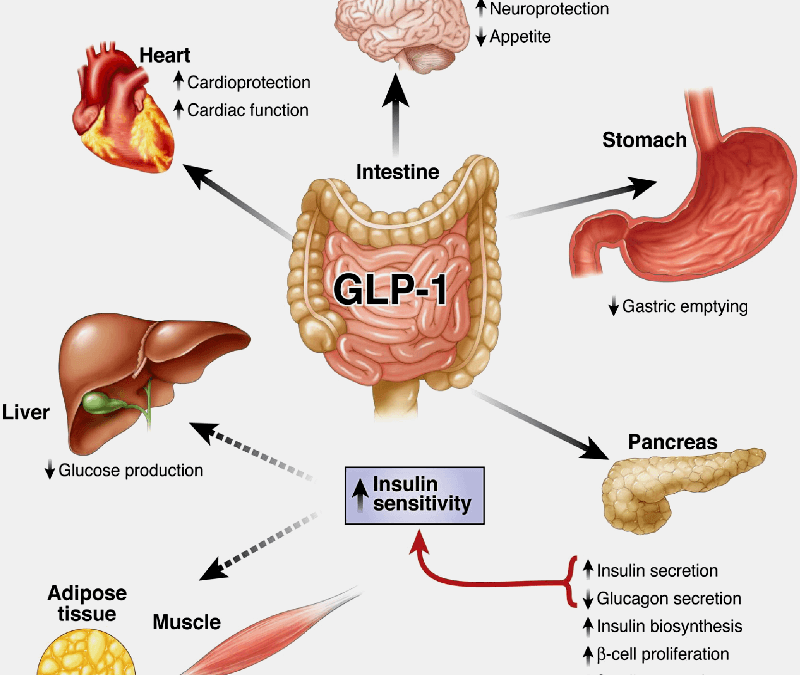
GLP-1, or Glucagon-Like Peptide-1, is an incretin hormone produced by the intestinal L-cells in response to food intake. It plays a crucial role in glucose metabolism by enhancing insulin secretion, inhibiting glucagon release, and slowing gastric emptying. These actions collectively help maintain blood sugar levels and promote satiety.
Functions of GLP-1
Stimulates Insulin Secretion: Enhances insulin release in response to meals.
Inhibits Glucagon Release: Reduces glucagon levels, which decreases hepatic glucose production.
Promotes Satiety: Slows gastric emptying and promotes feelings of fullness.
Cardioprotective Effects: Has beneficial effects on cardiovascular health, including lowering blood pressure and reducing inflammation.
Understanding PYY
What is PYY?
PYY, or Peptide YY, is a gut hormone secreted by the L-cells in the ileum and colon post-meal. It is involved in reducing appetite and slowing down the digestive process. PYY works by signaling the brain’s appetite control centers, particularly the hypothalamus, to promote a feeling of fullness.
Functions of PYY
Reduces Appetite: Acts on the hypothalamus to decrease hunger.
Slows Gastric Emptying: Prolongs the digestion process to enhance satiety.
Inhibits Pancreatic Secretion: Affects digestive enzymes and fluid secretion from the pancreas.
Differences Between GLP-1 and PYY
While these two hormones share some functions, their primary roles and mechanisms differ significantly:
Primary Functions:
GLP-1: Primarily regulates blood sugar levels by enhancing insulin secretion and suppressing glucagon release.
PYY: Primarily regulates appetite and food intake by acting on the brain’s hunger control centers.
Secretion Timing:
GLP-1: Secreted immediately after food intake with a shorter half-life.
PYY: Levels peak postprandially and remain elevated longer to sustain satiety.
Metabolic Effects:
GLP-1: Directly influences insulin and glucagon secretion.
PYY: Has a more pronounced role in reducing appetite with less direct impact on glucose metabolism.
Similarities Between GLP-1 and PYY
Despite their differences, these two hormones share some common characteristics:
Origin: Both are secreted by intestinal L-cells in response to food intake.
Role in Satiety: Both contribute to the regulation of appetite and promote satiety.
Gastrointestinal Effects: Both slow gastric emptying, which helps prolong digestion and enhances feelings of fullness.
Dietary Ways to Upregulate GLP-1 and PYY
Polyphenol-Rich Foods
Examples: Apples, berries, green/black tea, dark chocolate.
Benefits: Polyphenols can enhance GLP-1 secretion, improve insulin sensitivity, and possess anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
Protein-Rich Foods
Examples: Lean meats, fish, eggs, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
Benefits: High-protein foods stimulate the release of PYY and GLP-1, helping to control appetite and improve glucose metabolism.
High-Fiber Foods
Examples: Whole grains, legumes, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds.
Benefits: Dietary fiber slows digestion, promotes the release of both PYY and GLP-1, enhances satiety, and stabilizes blood sugar levels.
Capsaicin
Examples: Chili peppers.
Benefits: Capsaicin has been shown to increase GLP-1 secretion and enhance satiety.
Resveratrol
Examples: Red grapes, red wine, peanuts, and blueberries.
Benefits: Resveratrol can stimulate the release of GLP-1 and improve insulin sensitivity.
Soy Isoflavones
Examples: Soybeans, tofu, tempeh, soy milk.
Benefits: Soy isoflavones can enhance PYY secretion, improve insulin sensitivity, and promote satiety.
Dairy Compounds
Examples: Milk, cheese, yogurt, and whey.
Benefits: Casein and whey proteins in dairy products increase PYY levels, promote satiety, and regulate appetite.
Specific Fiber Sources
1. Beta-Glucan:
Sources: Oats, barley.
Benefits: Beta-glucan is a soluble fiber that promotes the release of GLP-1 and PYY, improving satiety and blood sugar regulation.
2. Inulin:
Sources: Chicory root, garlic, onions, leeks, asparagus, bananas.
Benefits: Inulin is a prebiotic fiber that supports gut health and can enhance the secretion of GLP-1 and PYY.
3. Pectin’s:
Sources: Apples, citrus fruits, carrots, strawberries.
Benefits: pectins are soluble fibers that slow digestion and promote the release of satiety hormones like GLP-1 and PYY.
4. Resistant Starch:
Sources: Green bananas, cooked and cooled potatoes, legumes, whole grains.
Benefits: Resistant starch acts as a prebiotic and promotes the release of GLP-1 and PYY, enhancing satiety and metabolic health.
Lifestyle Modifications to Enhance GLP-1 and PYY Levels
Regular Physical Activity
Examples: Aerobic exercises (walking, running, cycling), resistance training, and yoga.
Benefits: Regular exercise can boost the levels of these two hormones, helping to regulate appetite and improve metabolic health.
Adequate Sleep
Importance: Proper sleep is essential for the optimal functioning of appetite-regulating hormones, including PYY and GLP-1.
Tips: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night, maintain a regular sleep schedule, and create a restful sleep environment.
Circadian Rhythms and Light Exposure: Circadian rhythms, which are influenced by exposure to natural light, play a crucial role in regulating various metabolic processes. Proper alignment of circadian rhythms can improve metabolic health, which in turn could potentially influence the secretion of hormones like GLP-1 and PYY.
Tips: Aim to get sunlight exposure (outside) early in the morning (sunrise if possible) and evening sun (sunset if possible) as often as you can. Avoid artificial light at night as a hard rule.
Stress Management
Techniques: Meditation, deep breathing exercises, mindfulness practices, hobbies.
Benefits: Reducing stress can positively affect hormone levels and appetite regulation, supporting overall health and weight management.
Conclusion
Understanding the roles of PYY and GLP-1 in regulating appetite and metabolism provides valuable insights into managing weight and improving overall health. By incorporating specific dietary choices and lifestyle modifications, such as consuming polyphenol-rich foods, increasing protein and fiber intake, and engaging in regular physical activity, you can effectively upregulate these hormones. These strategies not only promote satiety and regulate blood sugar levels but also support sustainable weight loss and metabolic health. By making informed choices, you can harness the power of PYY and GLP-1 to achieve your health and weight management goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are GLP-1 and Peptide Y?
GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1) and PYY (Peptide YY) are hormones produced by the gut in response to food intake. GLP-1 helps regulate blood sugar levels and promotes satiety, while Peptide YY reduces appetite and slows down the digestive process.
2. How do GLP-1 and Peptide YY differ in their functions?
GLP-1 primarily regulates blood sugar levels by enhancing insulin secretion and suppressing glucagon release. Peptide YY mainly regulates appetite by acting on the brain’s hunger control centers and slowing gastric emptying.
3. Can specific foods help increase GLP-1 and Peptide YY levels?
Yes, certain foods, such as polyphenol-rich fruits, high-protein foods, high-fiber foods, and compounds like capsaicin, resveratrol, soy isoflavones, and dairy proteins, can help increase the levels of GLP-1 and Peptide YY.
4. How does exercise influence GLP-1 and Peptide YY levels?
Regular physical activity can boost the levels of both GLP-1 and Peptide YY, helping to regulate appetite and improve metabolic health.
5. What role does sleep play in regulating GLP-1 and Peptide YY?
Adequate sleep is essential for the optimal functioning of appetite-regulating hormones, including GLP-1 and Peptide YY. Quality sleep helps maintain proper hormone levels and supports overall health.
6. How can stress management impact GLP-1 and Peptide YY levels?
Reducing stress through techniques like meditation, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness practices can positively affect hormone levels and appetite regulation, supporting overall health and weight management.
7. Are there any supplements that can help increase GLP-1 and Peptide YY levels?
While a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle are the best ways to increase GLP-1 and Peptide YY levels, some supplements containing fiber, protein, or specific compounds like resveratrol may help. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplements.
References
Polyphenols and GLP-1
Soy Isoflavones and PYY
Casein and Satiety
Whey Protein and PYY
Beta-Glucan and GLP-1
Inulin and Satiety Hormones
Pectins and Satiety
Resistant Starch and Satiety Hormones
Capsaicin and GLP-1
Naringenin and GLP-1
GLP-1 Functions
PYY Functions
Incretin Hormones and Their Roles
Appetite Regulation by Gut Hormones